Stop Guessing! The Visual Protein Cheat Sheet: How to Eyeball 25 Grams of Protein (No Scale Needed)
The 85% Problem: Why We Can’t Trust Our Eyes
Did you know? About 85% of people completely miscalculate their food portions! It’s not your fault. Our eyes have been trained by giant plates and supersized restaurant meals.
As a Nurse Practitioner, I consistently recommend my weight loss patients follow a high-protein diet. Why? Because adequate protein intake (around 1.6 g per kg of recommended body weight) is crucial for preserving precious muscle mass while you're in a calorie deficit, and it's simply the most satisfying nutrient.
The easiest hack? Learn to eyeball your protein. That’s why I created a Visual Protein Cheat Sheet. It uses simple, everyday objects (like a deck of cards or your palm) to help you accurately estimate 25 – 35 grams of protein per meal—the golden target for effective weight loss and muscle maintenance.
The Golden Rule: Why You Need 25 go 35g of Protein Per Meal
Before we dive into the visuals, let's quickly reinforce why hitting this protein target is so vital. This target is designed to overcome common nutritional challenges, especially when managing appetite on medications like GLP-1s.
Scientific Necessity: Preserving Muscle
While some older research suggested the body could only utilize 20 grams of protein at a time, we now know that the actual "ceiling" is much higher with real-world, mixed meals (which contain fat and fiber).
We target 25 to 35 grams per meal not as a rigid limit, but as a guaranteed dose:
Trigger Anabolism: This amount provides the necessary surplus of amino acids to definitively trigger maximum Muscle Protein Synthesis (MPS). We use the higher end (30g+) to ensure the signal is strong enough, accounting for slower digestion and the higher protein needs associated with longevity and a calorie deficit.
Quality of Weight Loss: As a Nurse Practitioner, my priority is ensuring you lose fat, not muscle. Hitting this target protects your muscle mass, which preserves your metabolism and long-term health.
The Strategy: Maximum Satiety and Consistent Dosing
Maximum Satiety: Protein is the most filling macronutrient. Consistently hitting 25 to 35 g at breakfast and lunch is your best defense against cravings and helps prevent overconsumption at night.
Consistent Delivery: Don't save all your protein for dinner! Since whole food protein is absorbed slowly, spreading your intake across 3-4 eating occasions (meals and snacks) is the most effective strategy. This consistent dosing optimizes muscle repair and keeps your metabolism humming throughout the entire day.
The Visual Protein Cheat Sheet: Eyeball Your Portions
Our eyes are powerful tools for real-world scenarios. Here’s your guide to quickly estimate 25 to 35 g of protein using common visual cues.
1. 🥩 High-Value Meat & Seafood (The 20+g Crew)
These are your primary protein sources. The "deck of cards" is your universal size guide here!
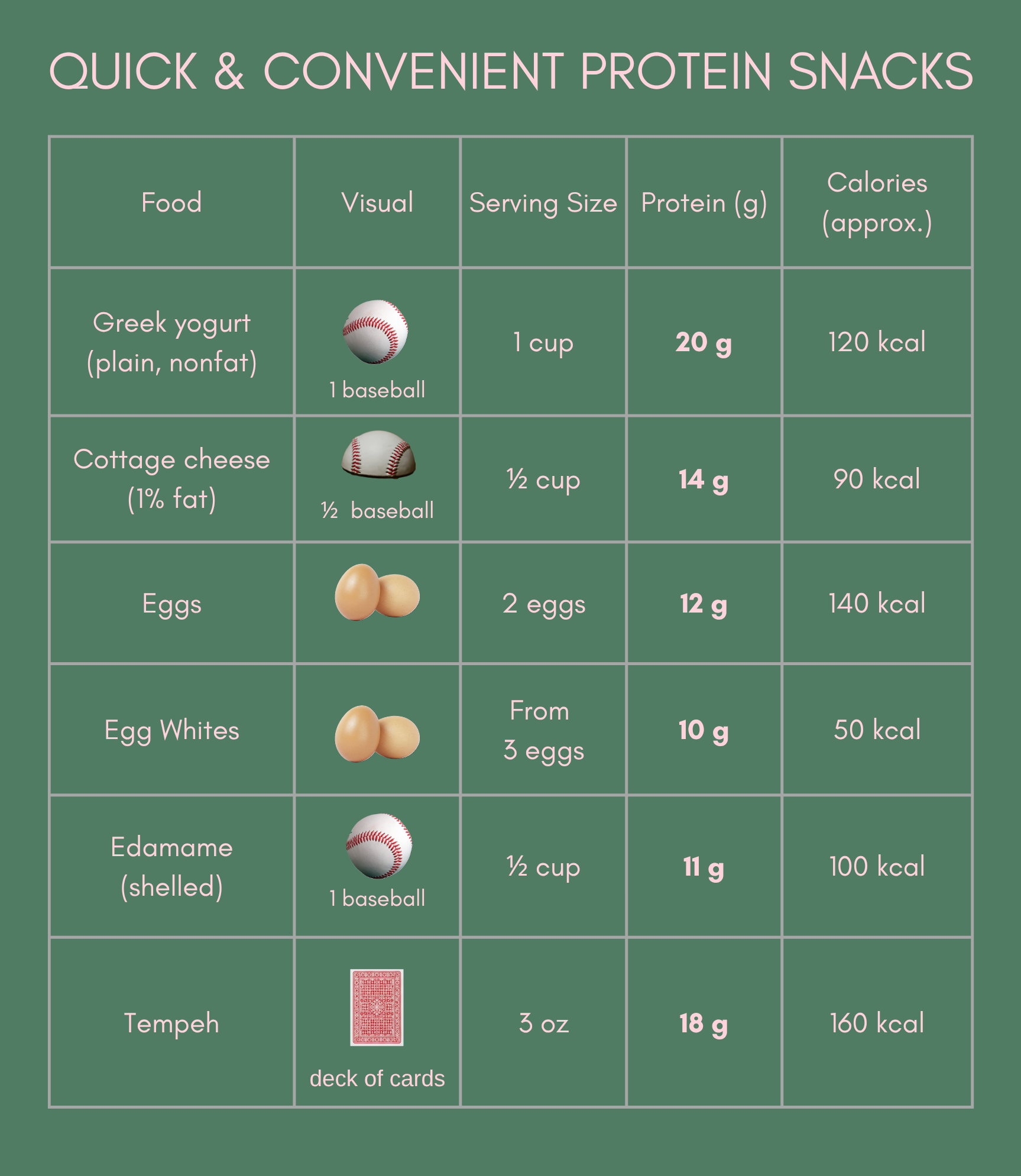
2. 🥛 Quick & Convenient Protein Snacks
These are your grab-and-go options for easy protein boosts throughout the day.
3. 🌱 Fiber-Rich Plant-Based & Side Proteins
Great options for plant-based meals or boosting the protein and fiber in any dish.
Conclusion & Next Steps
Tracking doesn't always require equipment; it simply requires a few smart visual references. By confidently estimating your protein intake, you can protect your hard-earned muscle and stay fuller for longer—all without needing a scale!
Get Your FREE Printable PDF!
Want this Protein Cheat Sheet handy on your phone? Email me at alexis@silencemedical.info to receive a free, downloadable PDF version of this guide to save directly to your device!
Sources
Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. (2025). Portion control.
Mamerow, M. M., et al. (2014). Dietary protein distribution positively influences 24-h muscle protein synthesis in healthy adults. The Journal of Nutrition, 144(6), 876–880.
Morton, R. W., et al. (2018). A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression of the effect of protein supplementation on resistance training-induced gains in muscle mass and strength in healthy adults. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 52(6), 376–384.
U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. (2024). FoodData Central.